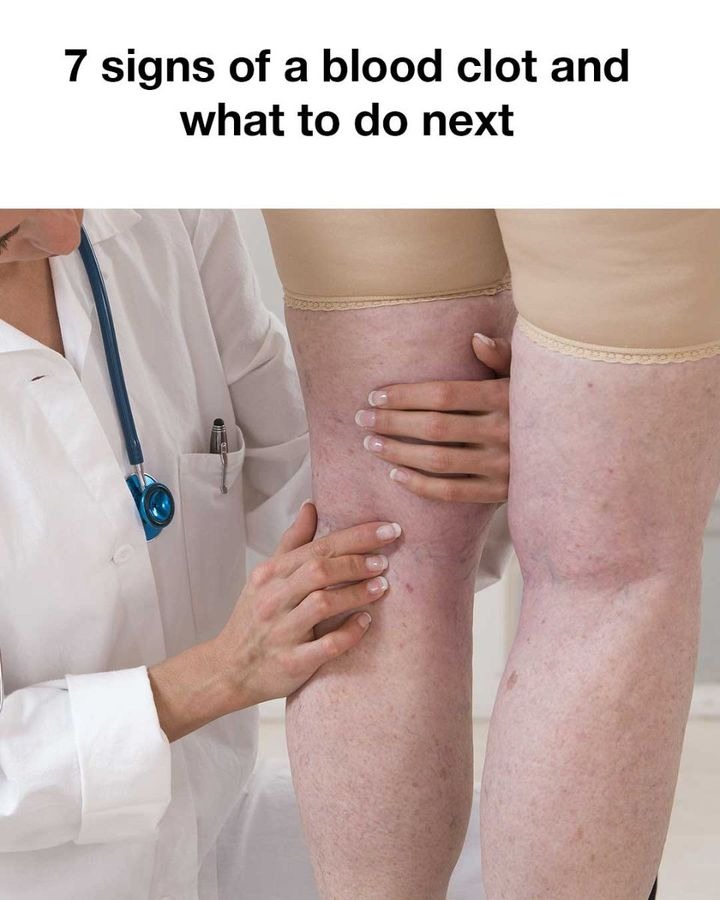
Blood clots can be life-threatening if not treated promptly. While blood clotting is a normal and essential process that prevents excessive bleeding after injury, abnormal clots forming inside veins or arteries can block blood flow and lead to serious complications.
According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), blood clots in deep veins — known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT) — can travel to the lungs and cause a pulmonary embolism (PE), a medical emergency.
Understanding the symptoms can help you recognize when to seek urgent medical care.
What Is a Blood Clot?
A blood clot (thrombus) is a gel-like mass formed by platelets and fibrin in response to injury. Problems arise when clots develop without injury or fail to dissolve properly.
Common clot-related conditions include:
-
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Usually occurs in the legs.
-
Pulmonary Embolism (PE): Occurs when a clot travels to the lungs.
-
Arterial clots: Can lead to heart attack or stroke.
7 Common Signs of a Blood Clot
Symptoms vary depending on where the clot forms. Below are widely recognized warning signs reported by major health authorities.
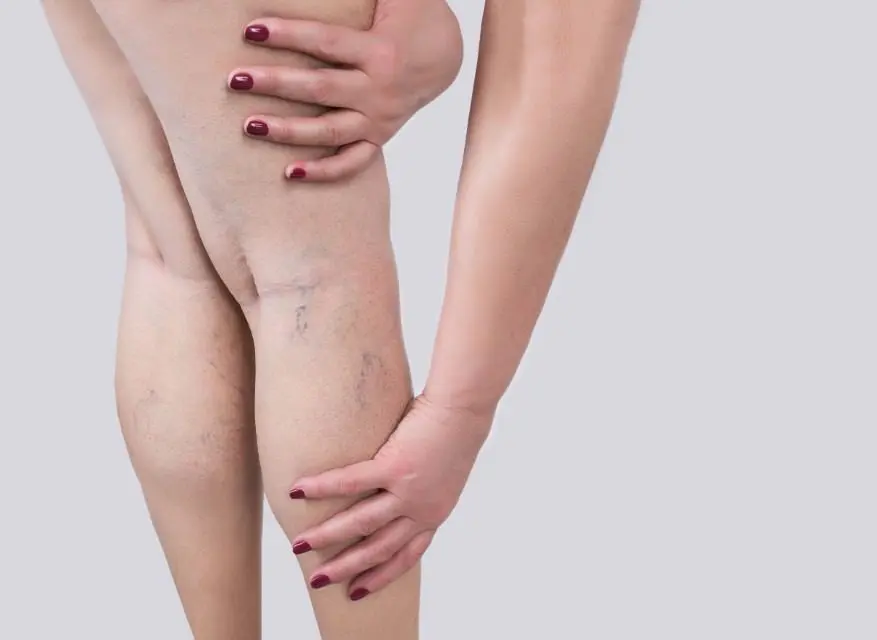
1. Swelling in One Limb
Unexplained swelling — especially in one leg — may indicate DVT. The swelling often develops suddenly and typically affects only one side.
This happens because the clot blocks normal blood return, causing fluid buildup in surrounding tissues.

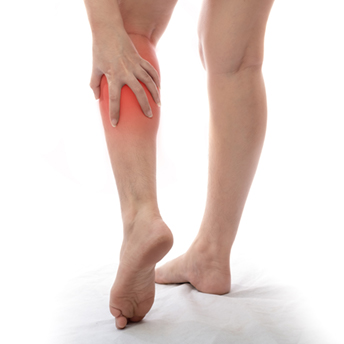
2. Leg Pain or Tenderness
Pain in the calf or thigh that feels like cramping, soreness, or pressure may be a sign of DVT. The discomfort often worsens when standing or walking.
Because it can resemble a muscle strain, persistent or worsening pain should be medically evaluated.
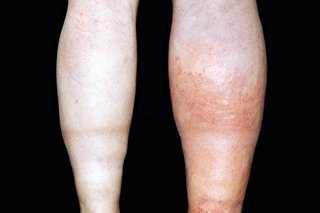
3. Skin Discoloration
Red, bluish, or purplish skin over the affected area can occur when circulation is impaired. The area may also appear slightly shiny.
4. Warmth Over the Area
The skin above a clot may feel warmer than surrounding tissue. This is related to inflammation caused by blocked blood flow.
5. Sudden Shortness of Breath
If a clot travels to the lungs (pulmonary embolism), sudden difficulty breathing can occur. This symptom requires immediate emergency care.
6. Chest Pain That Worsens With Breathing
Sharp chest pain, especially when taking deep breaths or coughing, may signal a pulmonary embolism.
Seek emergency medical attention immediately if this occurs.
7. Rapid Heart Rate
A fast or irregular heartbeat can develop when the body is under stress from a clot in the lungs.
When combined with shortness of breath or chest pain, this is considered a medical emergency.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Call emergency services immediately if you experience:
-
Sudden shortness of breath
-
Chest pain
-
Fainting
-
Rapid heartbeat with other symptoms
If you suspect DVT (leg swelling, pain, warmth), contact a healthcare provider promptly for evaluation.
Medical professionals may use:
-
Ultrasound imaging
-
CT scan (for suspected pulmonary embolism)
-
Blood tests such as D-dimer
Treatment commonly includes anticoagulant medications (“blood thinners”) to prevent clot growth. In certain cases, clot-dissolving therapy or procedures may be required.
Risk Factors for Blood Clots
According to the CDC and American Heart Association, risk factors include:
-
Prolonged immobility (long travel, hospitalization)
-
Recent surgery
-
Cancer
-
Pregnancy
-
Hormone therapy
-
Smoking
-
Obesity
-
Personal or family history of clotting disorders
Prevention Tips
While not all clots can be prevented, you can reduce risk by:
-
Staying physically active
-
Avoiding prolonged sitting
-
Drinking adequate fluids
-
Managing chronic conditions
-
Following prescribed preventive medications if at high risk
Final Takeaway
Blood clots are serious but treatable when identified early. Recognizing symptoms and seeking timely medical care can significantly reduce the risk of complications.
If you experience warning signs, do not delay medical evaluation.
Disclaimer:
This content is for informational purposes only and does not replace professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider with questions about your health.